Security & Compliance
- Security \& Compliance
- AWS Shared Responsibility Model
- DDOS Protection on AWS
- AWS Shield
- AWS WAF - Web Application Firewall
- Penetration Testing on AWS Cloud
- Data at rest vs. Data in transit
- AWS KMS (Key Management Service)
- AWS CloudHSM
- Types of Customer Master Keys: CMK
- AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
- AWS Secrets Manager
- AWS Artifact
- AWS GuardDuty
- AWS Inspector
- AWS Config
- Amazon Macie
- AWS Security Hub
- Amazon Detective
- AWS Abuse
- Root user privileges
- IAM Access Analyzer
- Summary
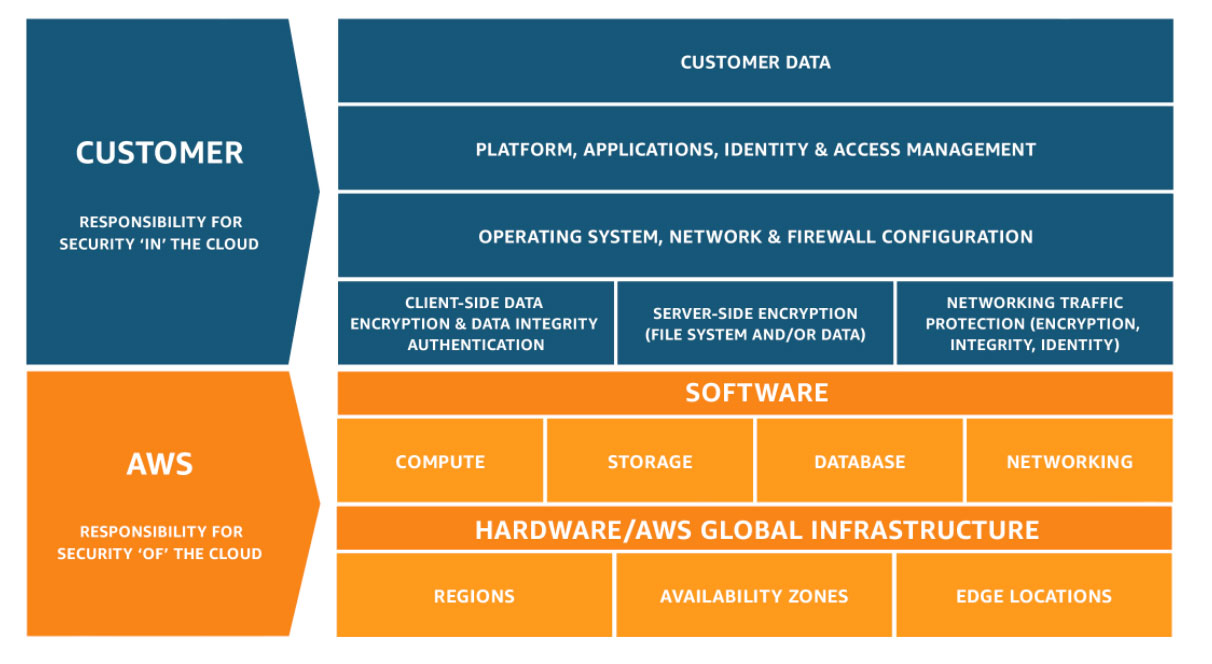
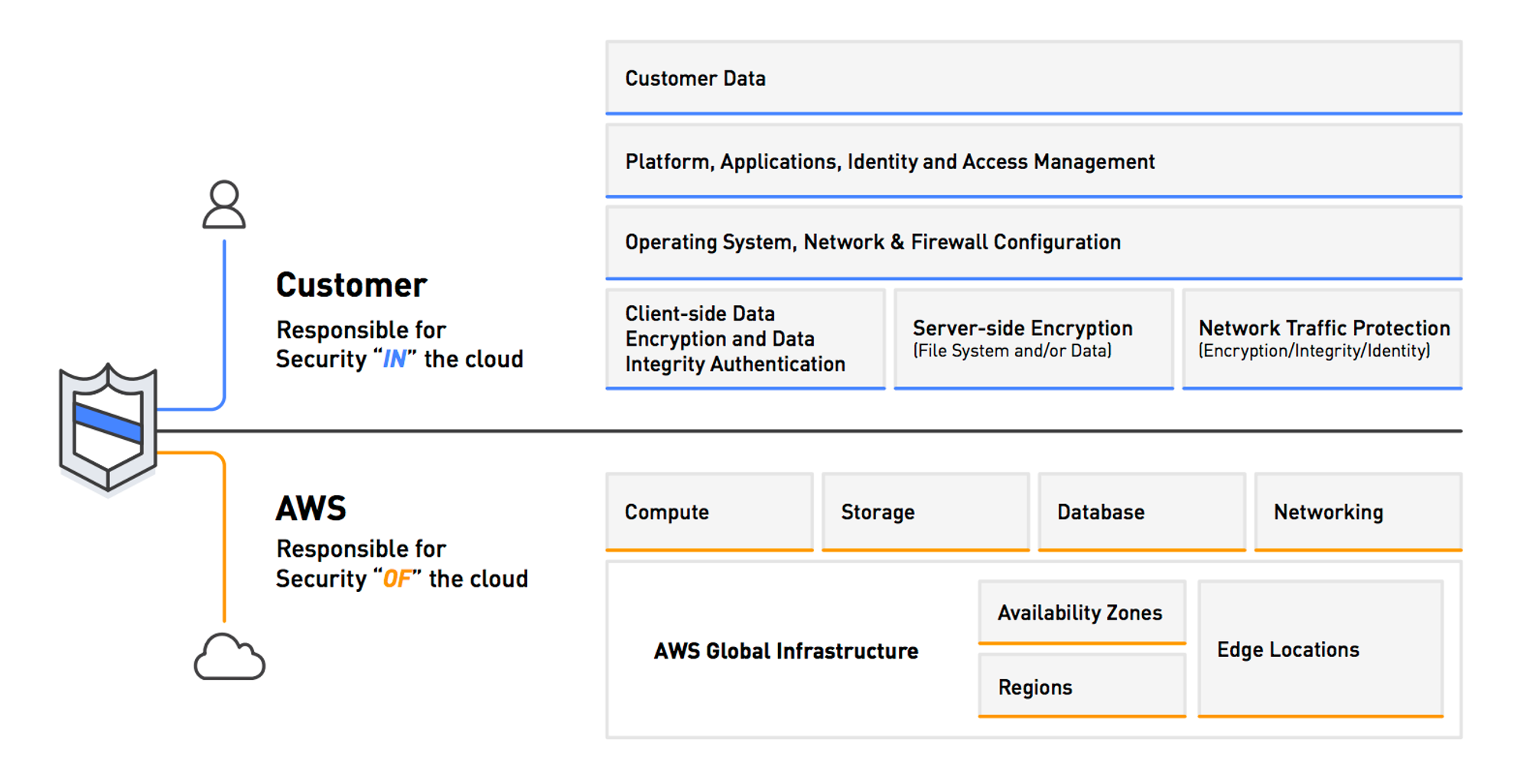
AWS Shared Responsibility Model
- AWS and customers share responsibilities for security and compliance.
- AWS: Responsible for the security of the cloud (infrastructure).
- Customer: Responsible for the security in the cloud (applications and data).
- Shared controls: Patch Management, Configuration Management, Awareness & Training
Shared Responsibility Categories
| Aspect | AWS Responsibility | Customer Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Physical security, hardware, and global network. | Not applicable (fully managed by AWS). |
| Configuration | Default configurations for services. | Customize configurations to meet security requirements. |
| Data Protection | Ensure data encryption capabilities are available. | Encrypt sensitive data and manage access permissions. |
| Patching | Patching underlying infrastructure. | Patching the operating system and applications. |
| Access Management | IAM service availability and best practices. | Defining and enforcing user and resource permissions. |
Example for RDS
- AWS Responsibility:
- Managing the underlying database engine (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL).
- Ensuring hardware security and network isolation.
- Applying patches to the database software.
- Audit the underlying instance and disks & guarantee it functions
- Customer Responsibility:
- Managing database credentials and access control.
- Encrypting data at rest and in transit.
- Defining backup and recovery policies.
- Monitoring database performance using CloudWatch.
- Ensure parameter groups or DB is configured to only allow SSL connections
Example for S3
- AWS Responsibility:
- Ensuring data durability and availability.
- Managing infrastructure security for S3.
- Guarantee you get unlimited storage
- Ensure AWS employees can’t access your data
- Ensure separation of the data between different customers
- Customer Responsibility:
- Configuring bucket policies, access control lists (ACLs), and IAM roles.
- Enabling encryption for objects (e.g., server-side or client-side encryption).
- Monitoring and auditing access using AWS CloudTrail and S3 access logs.
- Implementing versioning and lifecycle policies for object management.
DDOS Protection on AWS
- AWS Shield Standard: protects against DDOS attack for your website and applications, for all customers at no additional costs
- AWS Shield Advanced: 24/7 premium DDoS protection
- AWS WAF: Filter specific requests based on rules
- CloudFront and Route 53:
- Availability protection using global edge network
- Combined with AWS Shield, provides attack mitigation at the edge
- Be ready to scale – leverage AWS Auto Scaling
AWS Shield
- Prevents DDOS attack
- AWS Shield which protects against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks is available globally on Amazon CloudFront Edge Locations.
- Amazon EC2, Elastic Load Balancing (ELB), Amazon CloudFront, Amazon Route 53, AWS Global Accelerator provide automatic ddos protection.
- Provides protection from attacks such as SYN/UDP Floods, Reflection attacks and other layer 3/layer 4 attacks
- 24/7 access to AWS DDoS response team (DRP)
- Protect against higher fees during usage spikes due to DDoS
AWS WAF - Web Application Firewall
- Protects your web applications from common web exploits (Layer 7)
- Layer 7 is HTTP (vs Layer 4 is TCP)
- Deploy on Application Load Balancer, API Gateway, CloudFront
- Define Web ACL (Web Access Control List):
- Rules can include IP addresses, HTTP headers, HTTP body, or URI strings
- Protects from common attack - SQL injection and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Size constraints, geo-match (block countries)
- Rate-based rules (to count occurrences of events) – for DDoS protection
Penetration Testing on AWS Cloud
- AWS customers are welcome to carry out security assessments or penetration tests against their AWS infrastructure without prior approval for 8 services:
- Amazon EC2 instances, NAT Gateways, and Elastic Load Balancers
- Amazon RDS
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon Aurora
- Amazon API Gateways
- AWS Lambda and Lambda Edge functions
- Amazon Lightsail resources
- Amazon Elastic Beanstalk environments
- List can increase over time
- Prohibited Activities
- DNS zone walking via Amazon Route 53 Hosted Zones
- Denial of Service (DoS), Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), Simulated DoS, Simulated DDoS
- Port flooding
- Protocol flooding
- Request flooding (login request flooding, API request flooding)
- For any other simulated events, contact aws-security-simulatedevent@amazon.com
- Read more: https://aws.amazon.com/security/penetration-testing/
Data at rest vs. Data in transit
- At rest: data stored or archived on a device
- On a hard disk, on a RDS instance, in S3 Glacier Deep Archive, etc.
- In transit (in motion): data being moved from one location to another
- Transfer from on-premises to AWS, EC2 to DynamoDB, etc.
- Means data transferred on the network
- We want to encrypt data in both states to protect it!
- For this we leverage encryption keys
AWS KMS (Key Management Service)
- Anytime you hear “encryption” for an AWS service, it’s most likely KMS
- KMS = AWS manages the encryption keys for us
- Encryption Opt-in:
- EBS volumes: encrypt volumes
- S3 buckets: Server-side encryption of objects
- Redshift database: encryption of data
- RDS database: encryption of data
- EFS drives: encryption of data
- Encryption Automatically enabled:
- CloudTrail Logs
- S3 Glacier
- Storage Gateway
AWS CloudHSM
- It is a service to keep hardware-based crypto keys safe.
- Used to meet compliance requirements (FIPS 140-2 level 3 compliant).
- Offers customers a private, isolated HSM access.
- Provides the ability to integrate with AWS services (e.g. Amazon RDS, Amazon S3).
- CloudHSM is designed for applications with high performance and security requirements, especially for cryptographic operations.
- You manage your own encryption keys entirely (not AWS)
Types of Customer Master Keys: CMK
Customer Managed CMK
- Create, manage and used by the customer, can enable or disable
- Possibility of rotation policy (new key generated every year, old key preserved)
- Possibility to bring-your-own-key
AWS managed CMK
- Created, managed and used on the customer’s behalf by AWS
- Used by AWS services (aws/s3, aws/ebs, aws/redshift)
AWS owned CMK
- Collection of CMKs that an AWS service owns and manages to use in multiple accounts
- AWS can use those to protect resources in your account (but you can’t view the keys)
CloudHSM Keys (custom keystore)
- Keys generated from your own CloudHSM hardware device
- Cryptographic operations are performed within the CloudHSM cluster
AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
- Let’s you easily provision, manage, and deploy SSL/TLS Certificates
- Used to provide in-flight encryption for websites (HTTPS)
- Supports both public and private TLS certificates
- Free of charge for public TLS certificates
- Automatic TLS certificate renewal
- Integrations with (load TLS certificates on)
- Elastic Load Balancers
- CloudFront Distributions
- APIs on API Gateway
AWS Secrets Manager
- Enables applications, automated processes, and other AWS services to securely access confidential information.
- Provides a simple and automated way to return, manage and retrieve confidential information.
- It has the capacity to store sensitive data such as passwords and API keys for integration into AWS services or databases.
- Thanks to integration with AWS KMS (Key Management Service), confidential information is protected with strong encryption.
AWS Artifact
- AWS Artifact aims to provide access to security and compliance documentation and reports for AWS accounts.
- You can use these documents to support security controls and compliance requirements.
- Artifact Reports - Allows you to download AWS security and compliance documents from third-party auditors, like AWS ISO certifications, Payment Card Industry (PCI), and System and Organization Control (SOC) reports
- Artifact Agreements - Allows you to review, accept, and track the status of AWS agreements such as the Business Associate Addendum (BAA) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for an individual account or in your organization
- Can be used to support internal audit or compliance
AWS GuardDuty
- GuardDuty is used to automatically detect malicious activities and threats in your AWS accounts.
- Monitors security threats using anomaly-based detection techniques and provides real-time alerts.
- Can detect threats such as identity theft, network attacks and behavioral analysis.
- Quickly detects potential threats with threat data and behavioral analysis.
- Intelligent Threat discovery to Protect AWS Account
- Uses Machine Learning algorithms, anomaly detection, 3rd party data
- One click to enable (30 days trial), no need to install software
- Input data includes:
- CloudTrail Events Logs – unusual API calls, unauthorized deployments
- CloudTrail Management Events – create VPC subnet, create trail, …
- CloudTrail S3 Data Events – get object, list objects, delete object, …
- VPC Flow Logs – unusual internal traffic, unusual IP address
- DNS Logs – compromised EC2 instances sending encoded data within DNS queries
- Kubernetes Audit Logs – suspicious activities and potential EKS cluster compromises
- Can setup CloudWatch Event rules to be notified in case of findings
- CloudWatch Events rules can target AWS Lambda or SNS
- Can protect against CryptoCurrency attacks (has a dedicated “finding” for it)
AWS Inspector
- AWS Inspector is a service that automatically evaluates the security and compliance of your applications on AWS.
- This service scans your applications and identifies potential security vulnerabilities and compatibility issues.
- Creates reports and makes suggestions about detected vulnerabilities and incompatibilities.
- For EC2 instances
- Leveraging the AWS System Manager (SSM) agent
- Analyze against unintended network accessibility
- Analyze the running OS against known vulnerabilities
- For Containers push to Amazon ECR
- Assessment of containers as they are pushed
- Reporting & integration with AWS Security Hub
- Send findings to Amazon Event Bridge
What does AWS Inspector evaluate?
- Remember: only for EC2 instances and container infrastructure
- Continuous scanning of the infrastructure, only when needed
- Package vulnerabilities (EC2 & ECR) – database of CVE
- Network reachability (EC2)
- A risk score is associated with all vulnerabilities for prioritization
AWS Config
- Helps with auditing and recording compliance of your AWS resources
- Helps record configurations and changes over time
- Possibility of storing the configuration data into S3 (analyzed by Athena)
- Questions that can be solved by AWS Config:
- Is there unrestricted SSH access to my security groups?
- Do my buckets have any public access?
- How has my ALB configuration changed over time?
- You can receive alerts (SNS notifications) for any changes
- AWS Config is a per-region service
- Can be aggregated across regions and accounts
- View compliance of a resource over time
- View configuration of a resource over time
- View CloudTrail API calls if enabled
Amazon Macie
- Amazon Macie is a fully managed data security and data privacy service that uses machine learning and pattern matching to discover and protect your sensitive data in AWS.
- Macie helps identify and alert you to sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII)
AWS Security Hub
- Central security tool to manage security across several AWS accounts and automate security checks
- Integrated dashboards showing current security and compliance status to quickly take actions
- Automatically aggregates alerts in predefined or personal findings formats from various AWS services & AWS partner tools:
- GuardDuty
- Inspector
- Macie
- IAM Access Analyzer
- AWS Systems Manager
- AWS Firewall Manager
- AWS Partner Network Solutions
- Must first enable the AWS Config Service
Amazon Detective
- GuardDuty, Macie, and Security Hub are used to identify potential security issues, or findings
- Sometimes security findings require deeper analysis to isolate the root cause and take action – it’s a complex process
- Amazon Detective analyzes, investigates, and quickly identifies the root cause of security issues or suspicious activities (using ML and graphs)
- Automatically collects and processes events from VPC Flow Logs, CloudTrail, GuardDuty and create a unified view
AWS Abuse
- Report suspected AWS resources used for abusive or illegal purposes
- Abusive & prohibited behaviors are:
- Spam – receiving undesired emails from AWS-owned IP address, websites & forums spammed by AWS resources
- Port scanning – sending packets to your ports to discover the unsecured ones
- DoS or DDoS attacks – AWS-owned IP addresses attempting to overwhelm or crash your servers/softwares
- Intrusion attempts – logging in on your resources
- Hosting objectionable or copyrighted content – distributing illegal or copyrighted content without consent
- Distributing malware – AWS resources distributing software to harm computers or machines
- Contact the AWS Abuse team: AWS abuse form, or abuse@amazonaws.com
Root user privileges
- Root user = Account Owner (created when the account is created)
- Has complete access to all AWS services and resources
- Lock away your AWS account root user access keys!
- Do not use the root account for everyday tasks, even administrative tasks
- Actions that can be performed only by the root user:
- Change account settings (account name, email address, root user password, root user access keys)
- View certain tax invoices
- Close your AWS account
- Restore IAM user permissions
- Change or cancel your AWS Support plan
- Register as a seller in the Reserved Instance Marketplace
- Configure an Amazon S3 bucket to enable MFA
- Edit or delete an Amazon S3 bucket policy that includes an invalid VPC ID or VPC endpoint ID
- Sign up for GovCloud
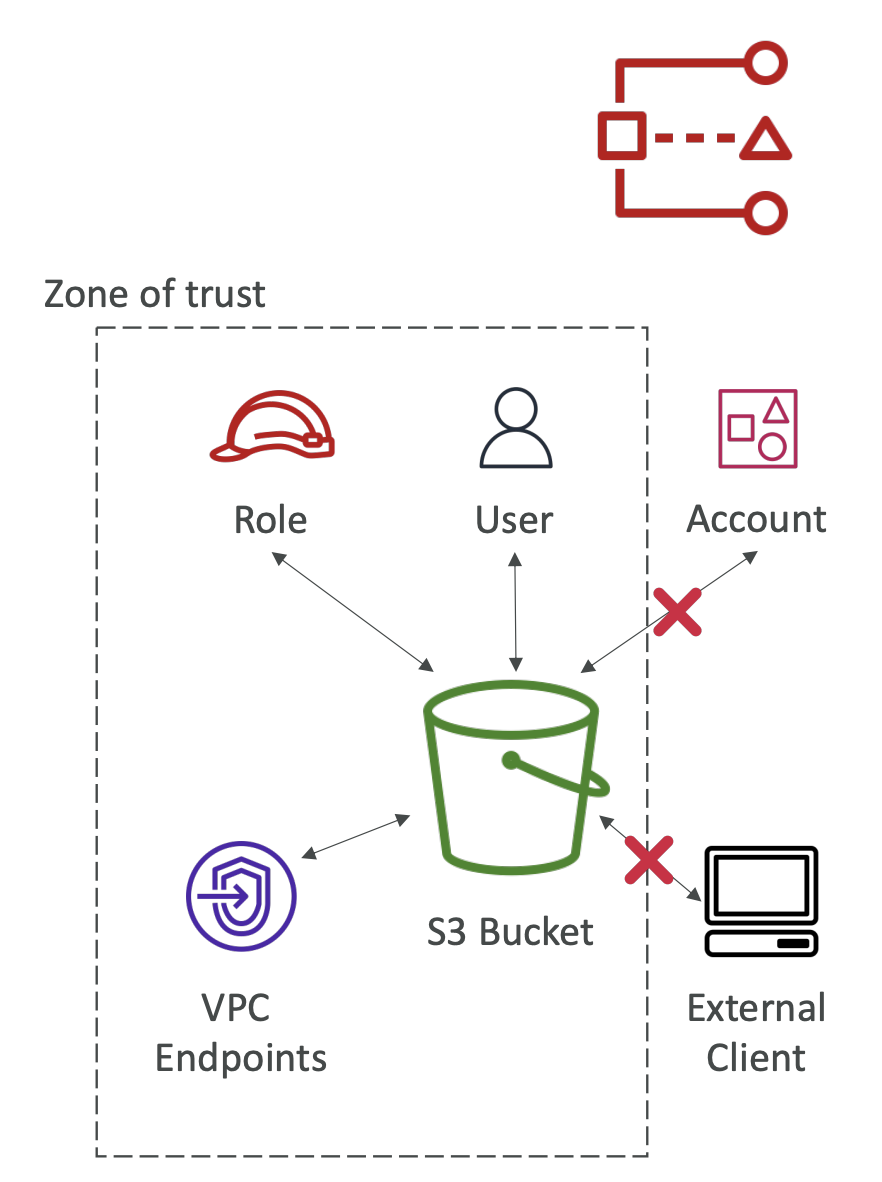
IAM Access Analyzer
- AWS IAM Access Analyzer is a tool that scans your AWS resource policies to find any unintended public or cross-account access. It helps you identify and fix security issues, ensuring that only authorized entities have access to your resources.
- Find out which resources are shared externally:
- S3 Buckets
- IAM Roles
- KMS Keys
- Lambda Functions and Layers
- SQS queues
- Secrets Manager Secrets
- Define Zone of Trust = AWS Account or AWS Organization.
- Access outside zone of trusts => findings
Summary
- Shared Responsibility on AWS
- Shield: Automatic DDoS Protection + 24/7 support for advanced
- WAF: Firewall to filter incoming requests based on rules
- KMS: Encryption keys managed by AWS
- CloudHSM: Hardware encryption, we manage encryption keys
- AWS Certificate Manager: provision, manage, and deploy SSL/TLS Certificates
- Artifact: Get access to compliance reports such as PCI, ISO, etc…
- GuardDuty: Find malicious behavior with VPC, DNS & CloudTrail Logs
- Inspector: For EC2 only, install agent and find vulnerabilities
- Config: Track config changes and compliance against rules
- Macie: Find sensitive data (ex: PII data) in Amazon S3 buckets
- CloudTrail: Track API calls made by users within account
- AWS Security Hub: gather security findings from multiple AWS accounts
- Amazon Detective: find the root cause of security issues or suspicious activities
- AWS Abuse: Report AWS resources used for abusive or illegal purposes
- Root user privileges:
- Change account settings
- Close your AWS account
- Change or cancel your AWS Support plan
- Register as a seller in the Reserved Instance Marketplace
You Can Purchase PDF : AWS Cloud Practitioner Study Notes (PDF)