EC2 Instance Storage
- EC2 Instance Storage
EBS Volumes
- AWS official Doc. https://docs.aws.amazon.com/ebs/latest/userguide/ebs-volumes.html
What’s an EBS Volume?
- Elastic Block Store (EBS) is a network-attached storage for EC2 instances.
- Provides persistent, block-level storage volumes.
- Can be used for databases, file systems, or applications requiring consistent, low-latency performance.
- It allows your instances to persist data, even after their termination
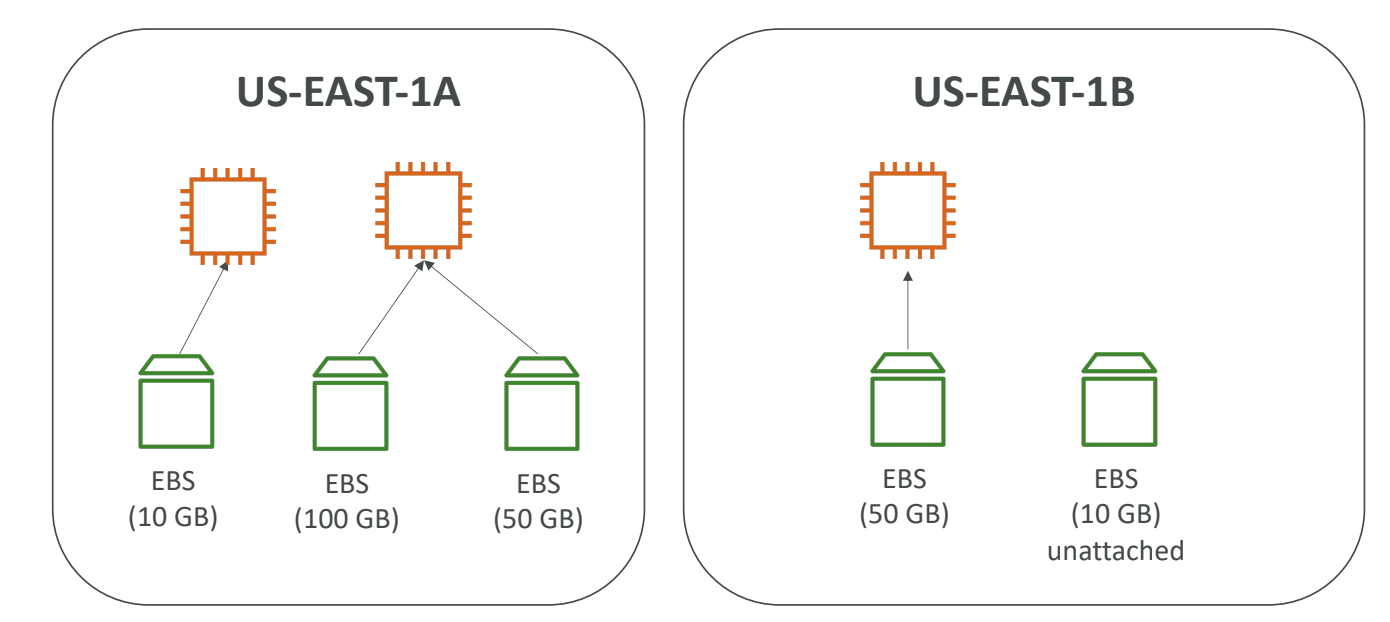
- They can only be mounted to one instance at a time
- They are bound to a specific availability zone
- Free tier: 30 GB of free EBS storage of type General Purpose (SSD) or Magnetic per month
EBS Volume
- Volumes are automatically replicated within an Availability Zone (AZ).
- Types include General Purpose (gp3/gp2), Provisioned IOPS (io1/io2), Throughput Optimized (st1), and Cold (sc1).
- Volumes can be attached to one EC2 instance at a time but can be detached and re-attached.
- Use case: preserve root volume when instance is terminated
EBS – Delete on Termination Attribute
- Controls whether the EBS volume is automatically deleted when the associated EC2 instance is terminated.
- By default, the root EBS volume is deleted (attribute enabled)
- By default, any other attached EBS volume is not deleted (attribute disabled)
- Can be enabled or disabled based on the need to persist data after instance termination.
EBS Snapshots
- Point-in-time backup of EBS volumes.
- Stored in Amazon S3 and can be used to restore or create new EBS volumes.
EBS Snapshots Features
- Incremental Backups: Only the blocks changed since the last snapshot are saved.
- Can be used across different regions or accounts by copying snapshots.
- Snapshots can be automated via Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager (DLM).
- EBS Snapshot Archive
- Move a Snapshot to an ”archive tier” that is 75% cheaper
- Takes within 24 to 72 hours for restoring the archive
- Recycle Bin for EBS Snapshots
- Setup rules to retain deleted snapshots so you can recover them after an accidental deletion
- Specify retention (from 1 day to 1 year)
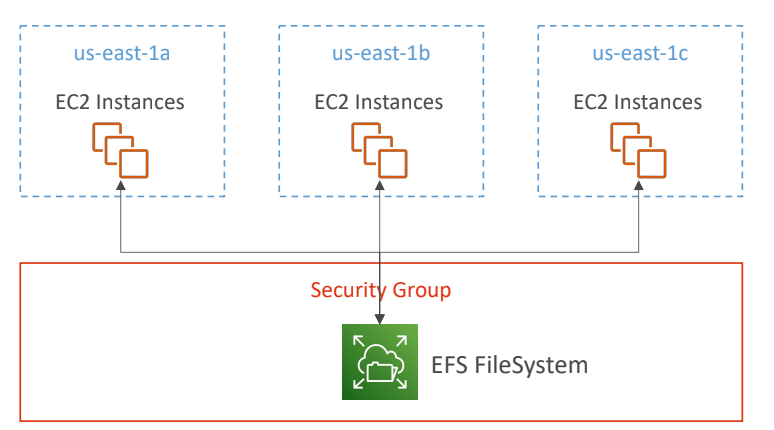
EFS: Elastic File System
- Fully managed NFS (Network File System) for EC2 instances that can be mounted on 100s of EC2.
- Can scale automatically as data grows.
- Accessible from multiple AZs, providing high availability and durability.
EFS Infrequent Access (EFS-IA)
- Lower-cost storage class for data not accessed frequently.
- Up to 92% lower cost compared to EFS Standard
- Allows cost savings by automatically moving infrequently accessed files to EFS-IA.
- Provides the same high availability as standard EFS.
- Example: move files that are not accessed for 60 days to EFS-IA
Amazon FSx – Overview
- Fully managed service providing file systems optimized for different workloads.
- Launch 3rd party high-performance file systems on AWS
- Fully managed service
- FSx for Lustre
- FSx for Windows File Server
- FSx for NetApp ONTAP
Amazon FSx for Windows File Server
- Provides fully managed file storage built on Windows Server.
- Supports SMB protocol & Windows NTFS
- Integration with Active Directory, and Windows-based applications.
- Can be accessed from AWS or your on-premise infrastructure
Amazon FSx for Lustre
- High-performance file system optimized for compute-heavy workloads.
- Designed for applications needing fast storage
- Like machine learning, high-performance computing, or video processing.
- Scales up to 100s GB/s, millions of IOPS, sub-ms latencies
EC2 Instance Store
- Ephemeral storage directly attached to the EC2 instance.
- EBS volumes are network drives with good but “limited” performance
- High I/O performance but non-persistent (data is lost when the instance stops or terminates).
- Ideal for temporary storage of data like caches, buffers, or temporary files.
- Good for buffer / cache / scratch data / temporary content
- Risk of data loss if hardware fails
- Backups and Replication are your responsibility
Shared Responsibility Model for EC2 Storage
| AWS Responsibilities | User Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Ensure durability and availability of EBS and EFS storage | Back up data via snapshots, EFS replication, etc. |
| Data replication within the AZ for EBS volumes | Manage access and encryption of storage resources |
| Provide encryption capabilities (KMS integration) | Apply encryption for sensitive data at rest |
| Replacing faulty hardware | Responsibility of any data on the drives |
AMI Overview
- Amazon Machine Image (AMI): Template used to launch EC2 instances.
- An AMI contains an operating system, application server, and applications.
- AMI are a customization of an EC2 instance
- You add your own software, configuration, operating system, monitoring…
- Faster boot / configuration time because all your software is pre-packaged
- AMI are built for a specific region (and can be copied across regions)
- You can launch EC2 instances from:
- A Public AMI: AWS provided
- Your own AMI: you make and maintain them yourself
- An AWS Marketplace AMI: an AMI someone else made (and potentially sells)
AMI Process (from an EC2 instance)
- Launch an EC2 instance.
- Configure the instance with applications or settings.
- Create an AMI from the running instance, which can be used to launch new EC2 instances with the same configuration.
EC2 Image Builder
- Automates the process of creating and maintaining custom AMIs.
- Helps create compliant, secure, and up-to-date machine images.
- Allows integration with services like AWS Systems Manager for automation and lifecycle management.
- Can be run on a schedule (weekly, whenever packages are updated, etc…)
- Free service (only pay for the underlying resources)
You Can Purchase PDF : AWS Cloud Practitioner Study Notes (PDF)