EC2: Virtual Machines
- EC2: Virtual Machines
What is Amazon EC2?
- Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is a scalable compute service that allows users to rent virtual servers in the cloud.
- It provides flexibility to scale compute resources up or down based on demand, offering a cost-effective solution for applications with variable workloads.
- Key features include:
- On-Demand Instances: Pay for compute capacity by the hour or second, with no long-term commitments.
- Reserved Instances: Make a one-time payment for a significant discount on instance usage over a one- or three-year term.
- Spot Instances: Bid for unused EC2 capacity at a potentially lower price, allowing cost savings for flexible workloads.
EC2 Sizing & Configuration Options
- EC2 allows for customized sizing and configurations, which include:
- Instance Type: Selecting the appropriate type based on the application’s performance requirements.
- Storage Options: Using Amazon EBS for persistent block storage or instance store for temporary storage.
- Networking: Configuring VPCs, subnets, and security groups to control access and manage traffic.
- Elastic Load Balancing: Distributing incoming traffic across multiple EC2 instances to enhance availability and fault tolerance.
- Auto Scaling: Automatically adjusting the number of instances based on demand, ensuring the application has the necessary resources.
EC2 User Data
- User data is a powerful feature for automating the setup of EC2 instances.
- It can be specified at instance launch and is executed on the instance when it first boots.
- bootstrapping means launching commands when a machine starts
- That script is only run once at the instance first start
- Common use cases include:
- Installing software packages (e.g.,
yum install httpd -yfor Apache). - Downloading configuration files or scripts from Amazon S3.
- Configuring system settings and services (e.g., starting an application server).
- Installing software packages (e.g.,
EC2 Instance Types - Overview
Amazon EC2 offers a variety of instance types, each designed to meet specific application requirements.(https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/instance-types/)
General Purpose Instances
- General purpose instances provide a balanced mix of compute, memory, and network resources.
- They are suitable for a variety of workloads and can handle different application types effectively.
- Use Cases:
- Web servers and applications
- Small to medium-sized databases
- Development and testing environments
- Enterprise applications
| Instance Type | vCPUs | Memory (GiB) | Network Performance | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t4g.micro | 2 | 1 | Up to 5 Gigabit | EBS only |
| t3.micro | 2 | 1 | Up to 5 Gigabit | EBS only |
| m5.large | 2 | 8 | Up to 10 Gigabit | EBS only |
| m5.xlarge | 4 | 16 | Up to 10 Gigabit | EBS only |
Compute Optimized Instances
- Compute optimized instances are designed for applications that require high-performance processors and are well-suited for compute-intensive workloads.
- Use Cases:
- High-performance web servers
- Batch processing
- Data analytics
- Machine learning inference
| Instance Type | vCPUs | Memory (GiB) | Network Performance | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| c5.large | 2 | 4 | Up to 10 Gigabit | EBS only |
| c5.xlarge | 4 | 8 | Up to 10 Gigabit | EBS only |
| c5.2xlarge | 8 | 16 | Up to 10 Gigabit | EBS only |
| c5n.9xlarge | 36 | 96 | 10 Gigabit | EBS only |
Memory Optimized Instances
- Memory optimized instances provide high memory bandwidth and are optimized for applications that require large amounts of memory.
- Use Cases:
- High-performance databases (e.g., SAP HANA)
- In-memory caches (e.g., Redis, Memcached)
- Real-time big data analytics
- Data mining applications
| Instance Type | vCPUs | Memory (GiB) | Network Performance | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r5.large | 2 | 16 | Up to 10 Gigabit | EBS only |
| r5.xlarge | 4 | 32 | Up to 10 Gigabit | EBS only |
| r5.4xlarge | 16 | 128 | Up to 10 Gigabit | EBS only |
| r5b.12xlarge | 48 | 384 | 10 Gigabit | EBS only |
Storage Optimized Instances
- Storage optimized instances are designed for applications that require high, sequential read and write access to large datasets.
- Use Cases:
- Data warehousing applications
- Hadoop distributed computing
- High-frequency trading applications
- NoSQL databases (e.g., Cassandra)
| Instance Type | vCPUs | Memory (GiB) | Network Performance | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| i3.large | 2 | 15 | Up to 10 Gigabit | 1 x 475 GB NVMe SSD |
| i3.xlarge | 4 | 30 | Up to 10 Gigabit | 1 x 950 GB NVMe SSD |
| i3.2xlarge | 8 | 61 | Up to 10 Gigabit | 1 x 1.9 TB NVMe SSD |
| d2.8xlarge | 36 | 244 | Up to 10 Gigabit | 12 x 2 TB HDD |
EC2 Instance Types: Example
Here’s a quick overview of some example instance types in each category, along with their characteristics:
| Instance Type | vCPUs | Memory (GiB) | Storage | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t3.micro | 2 | 1 | EBS only | General-purpose applications with burstable performance; suitable for low-traffic web servers or development environments. |
| c5.large | 2 | 4 | EBS only | Compute-intensive applications like gaming, web servers, and machine learning inference. |
| m5.xlarge | 4 | 16 | EBS only | Balanced workloads, such as small databases and caching fleets. Ideal for web applications. |
| r5.xlarge | 4 | 32 | EBS only | Memory-intensive applications such as databases, in-memory caches, and analytics workloads. |
| i3.2xlarge | 8 | 61 | 1 x 2.5 TB NVMe SSD | Storage-intensive applications like NoSQL databases, data warehousing, and big data analytics. |
| p3.2xlarge | 8 | 61 | EBS only | GPU-accelerated computing for machine learning, high-performance computing (HPC), and graphics-intensive applications. |
t2.micro is part of the AWS free tier (up to 750 hours per month)
Introduction to Security Groups
- Security Groups are virtual firewalls that control inbound and outbound traffic to Amazon EC2 instances.
- They act at the instance level, not the subnet level, and provide a way to manage access to resources within a VPC (Virtual Private Cloud).
- Security groups can be associated with multiple instances and can be modified at any time, allowing for flexible management of network access.
- Key Features:
- By default, all inbound traffic is denied, and all outbound traffic is allowed.
- You can specify rules based on protocol (TCP, UDP, ICMP), port number, and source IP address or CIDR block.
Common Use Cases
- Restricting access to an application server (allowing only specific IPs).
- Allowing traffic from specific ports (e.g., HTTP/HTTPS).
- Isolating database instances from public access.
Deeper Dive
- Inbound Rules: Define the traffic allowed into your instances.
- Outbound Rules: Define the traffic allowed out from your instances.
- Each rule includes:
- Type: The protocol used (e.g., HTTP, SSH).
- Protocol: The protocol number (TCP = 6, UDP = 17).
- Port Range: The port(s) affected by the rule.
- Source/Destination: The IP address or CIDR range from which traffic is allowed.
Security Groups Diagram
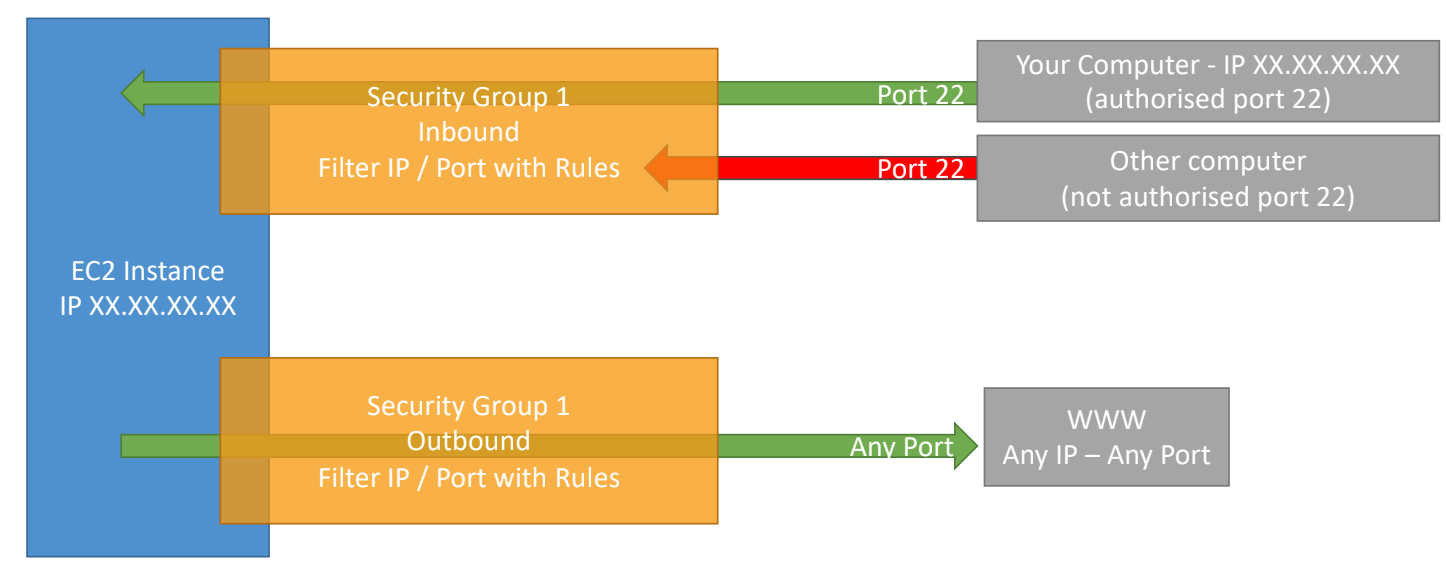
Examples of Security Group Rules
| Rule Type | Protocol | Port Range | Source/Destination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inbound Rule | TCP | 22 | 203.0.113.0/24 (SSH Access) |
| Inbound Rule | TCP | 80 | 0.0.0.0/0 (HTTP Access) |
| Outbound Rule | All Traffic | All | 0.0.0.0/0 |
Good to Know
- Limits: Each security group can have up to 60 inbound and 60 outbound rules by default (this limit can be increased by requesting through AWS Support).
- Default Security Group: When you create a VPC, a default security group is automatically created, which allows all outbound traffic and denies all inbound traffic by default.
- Multiple Security Groups: You can assign multiple security groups to a single EC2 instance, enabling fine-grained control over traffic.
- Security Best Practices:
- Apply the principle of least privilege (only allow necessary traffic).
- Regularly review and audit security group rules.
- Use descriptive names and tags for easy management.
Classic Ports to Know
| Port Number | Protocol | Service | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | TCP | FTP (Data Transfer) | Used for transferring files over FTP. |
| 21 | TCP | FTP (Control) | Used for controlling file transfer sessions. |
| 22 | TCP | SSH | Secure Shell for secure logins and command execution. |
| 80 | TCP | HTTP | Hypertext Transfer Protocol for web traffic. |
| 443 | TCP | HTTPS | Secure HTTP for secure web traffic. |
| 3389 | TCP | RDP | Used for Remote Desktop Protocol, allowing users to connect to and control remote Windows machines. |
EC2 Instance Launch Types
- On Demand Instances: short workload, predictable pricing
- Reserved: (1 & 3 years)
- Reserved Instances: long workloads
- Convertible Reserved Instances: long workloads with flexible instances
- Savings Plans (1 & 3 years): commitment to an amount of usage, long workload
- Spot Instances: short workloads, for cheap, can lose instances
- Dedicated Instances: no other customers will share your hardware
- Dedicated Hosts: book an entire physical server, control instance placement
- Capacity Reservations: reserve capacity in a specific AZ for any duration
On Demand Instance
- Pay for what you use:
- Linux or Windows - billing per second, after the first minute
- All other operating systems - billing per hour
- Has the highest cost but no upfront payment
- No long-term commitment
- Recommended for short-term and un-interrupted workloads, where you can’t predict how the application will behave
Reserved Instances
- Up to 72% discount compared to On-demand
- You reserve a specific instance attributes (Instance Type, Region, Tenancy, OS)
- Reservation Period – 1 year (+discount) or 3 years (+++discount)
- Payment Options – No Upfront (+), Partial Upfront (++), All Upfront (+++)
- Reserved Instance’s Scope – Regional or Zonal (reserve capacity in an AZ)
- Recommended for steady-state usage applications (think database)
-
You can buy and sell in the Reserved Instance Marketplace
- Convertible Reserved Instance
- Can change the EC2 instance type, instance family, OS, scope and tenancy
- Up to 66% discount
Savings Plans
- Get a discount based on long-term usage (up to 72% - same as RIs)
- Commit to a certain type of usage ($10/hour for 1 or 3 years)
-
Usage beyond EC2 Savings Plans is billed at the On-Demand price
- Locked to a specific instance family & AWS region (e.g., M5 in us-east-1)
- Flexible across:
- Instance Size (e.g., m5.xlarge, m5.2xlarge)
- OS (e.g., Linux, Windows)
- Tenancy (Host, Dedicated, Default)
Spot Instances
- Can get a discount of up to 90% compared to On-demand
- Instances that you can “lose” at any point of time if your max price is less than the current spot price
- The MOST cost-efficient instances in AWS
- Useful for workloads that are resilient to failure
- Batch jobs
- Data analysis
- Image processing
- Any distributed workloads
- Workloads with a flexible start and end time
- Not suitable for critical jobs or databases
Dedicated Hosts
- A physical server with EC2 instance capacity fully dedicated to your use
- Allows you to address compliance requirements and use your existing server- bound software licenses (per-socket, per-core, pe—VM software licenses)
- Purchasing Options:
- On-demand – pay per second for active Dedicated Host
- Reserved - 1 or 3 years (No Upfront, Partial Upfront, All Upfront)
- The most expensive option
- Useful for software that have complicated licensing model (BYOL – Bring Your Own License)
- Or for companies that have strong regulatory or compliance needs
Dedicated Instances
- Instances run on hardware that’s dedicated to you
- May share hardware with other instances in same account
- No control over instance placement (can move hardware after Stop / Start)
Capacity Reservations
- Reserve On-Demand instances capacity in a specific AZ for any duration
- You always have access to EC2 capacity when you need it
- No time commitment (create/cancel anytime), no billing discounts
- Combine with Regional Reserved Instances and Savings Plans to benefit from billing discounts
- You’re charged at On-Demand rate whether you run instances or not
- Suitable for short-term, uninterrupted workloads that needs to be in a specific AZ
EC2 Instance Launch Types Comparison
| Launch Type | Cost Structure | Payment Options | Commitment | Use Case | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| On-Demand Instances | - Linux/Windows: per second after the first minute - Other OS: billed per hour |
No upfront payment | No long-term commitment | Short-term and unpredictable workloads | High flexibility; can start/stop anytime |
| Reserved Instances | Up to 72% discount compared to On-Demand | - No Upfront - Partial Upfront - All Upfront |
1 year or 3 years | Steady-state applications (e.g., databases) | Reserved capacity in a specific region or AZ |
| Savings Plans | Up to 72% discount based on long-term usage | Commit to a certain usage amount | 1 year or 3 years | Applications with predictable usage patterns | Flexible across instance size, OS, and tenancy |
| Spot Instances | Discount up to 90% compared to On-Demand | Pay the Spot price | No commitment required | Cost-sensitive, resilient workloads (e.g., batch jobs) | Instances can be terminated anytime if spot price exceeds your max price |
| Dedicated Hosts | Most expensive; pay per second for active host | - On-Demand - Reserved (1 or 3 years) |
Long-term commitment possible | Compliance-heavy applications or complex licensing models | Full control over server; ideal for BYOL scenarios |
| Dedicated Instances | Higher than shared instances; not the most expensive | On-Demand pricing | No long-term commitment | Workloads needing dedicated hardware but can share resources | Limited control over instance placement |
| Capacity Reservations | Billed at On-Demand rates regardless of instance running | No upfront payment | No time commitment | Ensures EC2 capacity availability in a specific AZ | Can create/cancel anytime; no discounts on billing |
Which purchasing option is right for my use case?
- On-Demand Instances:
- Staying at a resort whenever we want and paying the full price for each night.
- Ideal for a startup running a web application with unpredictable traffic spikes.
- Reserved Instances:
- Planning a long vacation in advance, allowing us to get a significant discount for booking ahead.
- Best for a company operating a database server that requires constant uptime for a year.
- Savings Plans:
- Committing to a set amount per hour for a specified duration while enjoying any room type
- Suitable for a SaaS provider that anticipates steady usage of compute resources over three years.
- Spot Instances:
- Bidding for available rooms; the highest bidder secures the room, but they can be asked to leave at any moment.
- Perfect for a research team processing large data sets where jobs can be paused and resumed.
- Dedicated Hosts:
- Renting an entire wing of the resort exclusively for ourselves.
- Appropriate for a financial institution needing to comply with strict regulatory requirements and using custom software licenses.
- Dedicated Instances:
- Having a private room that’s solely ours but sharing some amenities with other guests.
- Great for a business running non-critical applications that need some level of hardware isolation.
- Capacity Reservations:
- Booking a room for a set period at full price, even if we don’t end up using it.
- Useful for an enterprise ensuring EC2 capacity for a new product launch in a specific availability zone.
Price Comparison Example – m4.large – us-east-1
| Launch Type | Hourly Price | Monthly Price (Approx.) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| On-Demand Instance | $0.096 per hour | $69.12 | Pay-as-you-go pricing. Ideal for short-term usage. |
| Reserved Instances | $0.054 per hour (1-year term) | $39.24 | Commit to one year for a significant discount. |
| Savings Plans | $0.058 per hour (1-year term) | $41.76 | Flexible savings plan applicable to any instance type. |
| Spot Instances | $0.028 per hour (varies with demand) | $20.16 | Pricing varies; can be interrupted. Best for flexible workloads. |
| Dedicated Hosts | $0.12 per hour (per host) | $86.40 | Dedicated physical server; pricing per host. |
| Dedicated Instances | $0.096 per hour | $69.12 | Similar to on-demand but on dedicated hardware. |
| Capacity Reservations | $0.096 per hour | $69.12 | Reserved capacity at on-demand pricing. |
Shared Responsibility Model for EC2
| Responsibility | AWS Responsibilities | User Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Security | The security of the underlying infrastructure, including hardware, software, networking, and facilities. | Securing the EC2 instances, including operating systems and applications. |
| Physical Security | Ensures physical security of data centers where EC2 instances run. | N/A |
| Network Security | Implements security measures for the network, including firewalls and DDoS protection. | Configuring security groups, network ACLs, and VPC settings. |
| Data Protection | Provides encryption options for data at rest and in transit. | Managing data encryption and access control. |
| Access Management | Offers IAM services to manage access to AWS resources. | Configuring IAM users, roles, and policies for access management. |
| Compliance | Complies with various compliance standards and certifications for infrastructure. | Compliance related to the applications and data hosted on EC2 instances. |
| Patch Management | Provides a secure and up-to-date infrastructure. | Applying patches and updates to the operating system and applications. |
EC2 Section – Summary
- EC2 Instance: AMI (OS) + Instance Size (CPU + RAM) + Storage + security groups + EC2 User Data
- Security Groups: Firewall attached to the EC2 instance
- EC2 User Data: Script launched at the first start of an instance
- SSH: start a terminal into our EC2 Instances (port 22)
- EC2 Instance Role: link to IAM roles
- Purchasing Options: On-Demand, Spot, Reserved (Standard + Convertible + Scheduled), Dedicated Host, Dedicated Instance
You Can Purchase PDF : AWS Cloud Practitioner Study Notes (PDF)