Databases & Analytics
- Databases \& Analytics
- Databases Intro
- Relational Databases (SQL)
- NoSQL Databases
- Databases \& Shared Responsibility on AWS
- AWS RDS Overview
- Amazon Aurora
- Amazon ElastiCache Overview
- DynamoDB
- Redshift Overview
- Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce)
- Amazon Athena
- Amazon QuickSight
- DocumentDB (with MongoDB Compatibility)
- Amazon Neptune
- Amazon QLDB
- Amazon Managed Blockchain
- AWS Glue
- DMS - Database Migration Service
- Databases \& Analytics Summary
Databases Intro
- Storing data on disk (EFS, EBS, EC2 Instance Store, S3) can have its limits
- Sometimes, you want to store data in a database…
- You can structure the data
- You build indexes to efficiently query / search through the data
- You define relationships between your datasets
- Databases are optimized for a purpose and come with different features, shapes and constraint
- Managed Databases: AWS takes care of maintenance, backups, and security for databases.
- Benefits: Reduced operational complexity, built-in high availability, disaster recovery, scalability, and enhanced security.
- Types:
- Relational Databases (SQL)
- NoSQL Databases
- Data Warehousing
- In-memory Caching
Relational Databases (SQL)
- Structured Data: Stored in predefined schema tables, managed with SQL.
- Use Cases: Transactional applications, financial systems.
- Examples: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, MariaDB.
NoSQL Databases
- Flexible Schema: No predefined schema, designed for fast and scalable data storage.
- Use Cases: Real-time applications, IoT, mobile apps.
- Benefits:
- Flexibility: easy to evolve data model
- Scalability: designed to scale-out by using distributed clusters
- High-performance: optimized for a specific data model
- Highly functional: types optimized for the data model
- Examples: DynamoDB, MongoDB (DocumentDB), Key-value, document, graph, in-memory, search databases
NoSQL data example: JSON
- JSON is a common form of data that fits into a NoSQL model
- Data can be nested
- Fields can change over time
- Support for new types: arrays, etc…
{
"name": "Abc",
"age": 30,
"cars": [
"Ford",
"BMW",
"Fiat"
],
"address": {
"type": "house",
"number": 23,
"street": "Abc Road"
}
}
Databases & Shared Responsibility on AWS
| AWS Responsibility | Customer Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure management, backups, patches | Data security, encryption, access controls (IAM) |
| Availability and failover | Data management, monitoring, performance tuning |
AWS RDS Overview
- RDS (Relational Database Service): Fully managed service for relational databases.
- It’s a managed DB service for DB use SQL as a query language.
- Supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, SQL Server.
- Handles backup, patching, high availability (Multi-AZ), and scaling.
Advantage over using RDS versus deploying DB on EC2
- RDS is a managed service:
- Automated provisioning, OS patching
- Continuous backups and restore to specific timestamp (Point in Time Restore)!
- Monitoring dashboards
- Read replicas for improved read performance
- Multi AZ setup for DR (Disaster Recovery)
- Maintenance windows for upgrades
- Scaling capability (vertical and horizontal)
- Storage backed by EBS (gp2 or io1)
- BUT you can’t SSH into your instances
RDS Deployments
- Read Replicas: Improves read performance, asynchronous replication.
- Multi-AZ: Automatic failover, high availability for production environments.
- Multi-Region: Disaster recovery across regions, global availability.
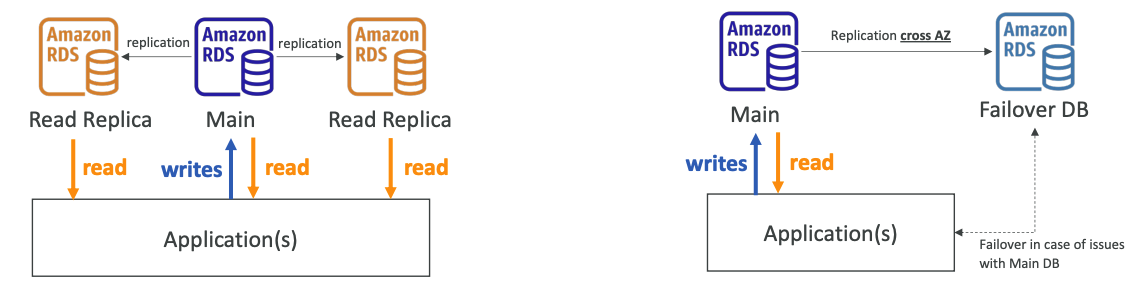
RDS Deployments: Read Replicas, Multi-AZ
| Read Replicas | Multi-AZ |
|---|---|
| Scale the read workload of your DB | Failover in case of AZ outage (high availability) |
| Can create up to 5 Read Replicas | Data is only read/written to the main database |
| Data is only written to the main DB | Can only have 1 other AZ as failover |
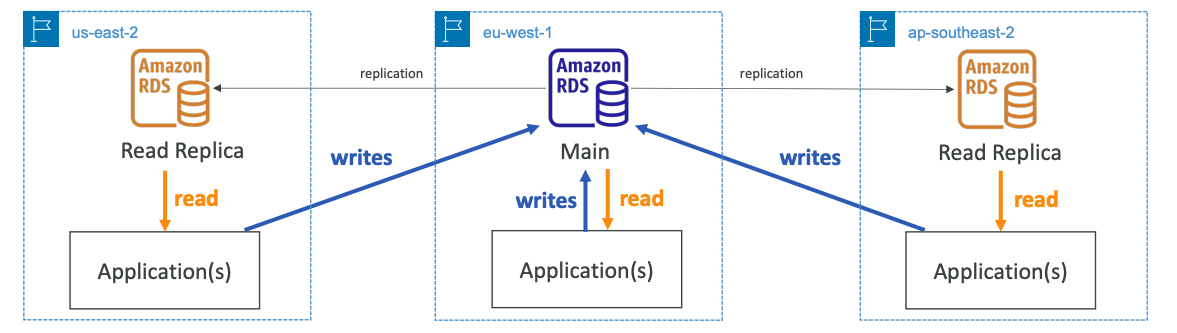
RDS Deployments: Multi-Region
- Multi-Region (Read Replicas)
- Disaster recovery in case of region issue
- Local performance for global reads
- Replication cost
Amazon Aurora
- Amazon Aurora: High-performance RDS database.
- Compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL.
- 5x faster than MySQL, 3x faster than PostgreSQL.
- Auto-scaling storage up to 64 TB.
- Supports Multi-AZ and up to 15 read replicas.
- Great for enterprise-grade applications requiring high availability and performance.
- Aurora costs more than RDS (20% more) – but is more efficient
Amazon ElastiCache Overview
- ElastiCache: In-memory data caching service.
- Redis: Advanced key-value store with replication and persistence.
- Memcached: Simple, memory-only caching service.
- Reduces database load and speeds up applications by caching frequent queries.
- Caches are in-memory databases with high performance, low latency
- AWS takes care of OS maintenance / patching, optimizations, setup, configuration, monitoring, failure recovery and backup
DynamoDB
- Fully managed, serverless NoSQL database.
- Supports key-value and document data models.
- Automatically scales based on demand.
- Provides high availability and durability with replication across 3 AZ
- Millions of requests per seconds, trillions of row, 100s of TB of storage
- Fast and consistent in performance
- Single-digit millisecond latency – low latency retrieval
- Integrated with IAM for security, authorization and administration
- Low cost and auto scaling capabilities
- Standard & Infrequent Access (IA) Table Class
DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX)
- In-memory caching for DynamoDB.
- 10x faster read performance. Single-digit millisecond latency to microseconds latency – when accessing your DynamoDB tables
- Secure, highly scalable & highly available
- Ideal for use cases where low-latency reads are critical.
DynamoDB Global Tables
- Multi-region replication for global applications.
- Low-latency reads and writes across multiple regions.
- Ensures data availability globally with multi-master replication.
Redshift Overview
- Managed data warehousing service.
- Optimized for online analytical processing (OLAP) and big data analytics.
- Uses columnar storage for fast query performance.
- 10x better performance than other data warehouses, scale to PBs of data
- Columnar storage of data (instead of row based)
- Supports integration with BI tools (QuickSight, Tableau).
- Massively Parallel Query Execution (MPP), highly available.
- Has a SQL interface for performing the queries.
- Pay-per-query or reserved instances for cost savings.
- Designed for massive datasets.
Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce)
- Managed big data processing service.
- Uses Hadoop, Apache Spark, and Hive for processing large data sets.
- Ideal for data transformation, machine learning, and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load).
- Integration with S3, DynamoDB, and Redshift.
- The clusters can be made of hundreds of EC2 instances
- EMR takes care of all the provisioning and configuration
- Auto-scaling and integrated with Spot instances
- Use cases: data processing, machine learning, web indexing, big data
Amazon Athena
- Serverless query service
- Use SQL to query structured and unstructured data stored in S3.
- No infrastructure to manage, pay-per-query.
- Supports various formats like CSV, JSON, Parquet, and ORC.
- Pricing: $5.00 per TB of data scanned
- Use compressed or columnar data for cost-savings (less scan)
- Use cases: Business intelligence / analytics / reporting, analyze & query VPC Flow Logs, ELB Logs, CloudTrail trails, etc…
- Analyze data in S3 using serverless SQL, use Athena
Amazon QuickSight
- Business Intelligence (BI) tool for data visualization.
- Serverless machine learning-powered business intelligence service to create interactive dashboards
- Fast, automatically scalable, embeddable, with per-session pricing
- Supports data from S3, Redshift, RDS, and other AWS data sources.
- Pay-per-session pricing model for cost efficiency.
- Use cases:
- Business analytics
- Building visualizations
- Perform ad-hoc analysis
- Get business insights using data
DocumentDB (with MongoDB Compatibility)
- Managed document database, MongoDB-compatible.
- DocumentDB is the same for MongoDB (which is a NoSQL database)
- Highly scalable and durable with Multi-AZ.
- Built for JSON document storage.
- Aurora storage automatically grows in increments of 10GB, up to 64 TB.
- Automatically scales to workloads with millions of requests per seconds
- Use cases: Content management, cataloging, and mobile backends.
Amazon Neptune
- Fully managed graph database
- A popular graph dataset would be a social network
- Users have friends
- Posts have comments
- Comments have likes from users
- Users share and like posts…
- Highly available across 3 AZ, with up to 15 read replicas
- Build and run applications working with highly connected datasets – optimized for these complex and hard queries
- Can store up to billions of relations and query the graph with milliseconds latency
- Highly available with replications across multiple AZs
- Great for knowledge graphs (Wikipedia), fraud detection, recommendation engines, social networking
Amazon QLDB
- QLDB stands for ”Quantum Ledger Database”
- A ledger is a book recording financial transactions
- Fully Managed, Serverless, High available, Replication across 3 AZ
- Used to review history of all the changes made to your application data over time
- Immutable system: no entry can be removed or modified, cryptographically verifiable
- 2-3x better performance than common ledger blockchain frameworks, manipulate data using SQL
- Difference with Amazon Managed Blockchain: no decentralization component, in accordance with financial regulation rules
Amazon Managed Blockchain
- Blockchain makes it possible to build applications where multiple parties can execute transactions without the need for a trusted, central authority.
- Amazon Managed Blockchain is a managed service to:
- Join public blockchain networks
- Or create your own scalable private network
- Compatible with the frameworks Hyperledger Fabric & Ethereum
AWS Glue
- Managed extract, transform, and load (ETL) service
- Useful to prepare and transform data for analytics
- Fully serverless service
- Glue Data Catalog: catalog of datasets
- can be used by Athena, Redshift, EMR
DMS - Database Migration Service
- Quickly and securely migrate databases to AWS, resilient, self healing
- The source database remains available during the migration
- Supports:
- Homogeneous migrations: ex Oracle to Oracle
- Heterogeneous migrations: ex Microsoft SQL Server to Aurora
Databases & Analytics Summary
- Relational Databases - OLTP: RDS & Aurora (SQL)
- Differences between Multi-AZ, Read Replicas, Multi-Region
- In-memory Database: ElastiCache
- Key/Value Database: DynamoDB (serverless) & DAX (cache for DynamoDB)
- Warehouse - OLAP: Redshift (SQL)
- Hadoop Cluster: EMR
- Athena: query data on Amazon S3 (serverless & SQL)
- QuickSight: dashboards on your data (serverless)
- DocumentDB: “Aurora for MongoDB” (JSON – NoSQL database)
- Amazon QLDB: Financial Transactions Ledger (immutable journal, cryptographically verifiable)
- Amazon Managed Blockchain: managed Hyperledger Fabric & Ethereum blockchains
- Glue: Managed ETL (Extract Transform Load) and Data Catalog service
- Database Migration: DMS
- Neptune: graph database
You Can Purchase PDF : AWS Cloud Practitioner Study Notes (PDF)